About the Technology
5G is the next-generation cellular standard after 4G. It is the fifth-generation cellular technology used for mobile communications. This cellular network can allow speeds up to 20 times faster than the previous 4G LTE technology it is replacing (Morales, 2022).
5G has been defined across several global standards such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) and European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). The official ITU specification, International Mobile Telecommunications-2020, targets maximum downlink and uplink throughputs of 20 Gbps and 10 Gbps, respectively; latency below 5 ms endpoint to Radio Access Network (RAN) and massive scalability, although initial deployments may be less ambitious. The new system architecture includes core network slicing and edge computing. (Gartner Glossary, n.d.)
According to MIDA (2022), the evolution of 1G to 5G in Malaysia took about 36 years since the introduction of wireless cellular technology as illustrated below:

DISCLAIMER:
This document has been prepared for internal circulation within MTDC. No part of this report should be reproduced, distributed or communicated to any third party without Data Insights Unit’s consent.
How Does 5G Change the World
According to Jowi Morales (2022), there are six ways that 5G is already changing the world, as explained below:
- Improving mobile connection
Faster data transfer is the basis of every cellular technology improvement. From 1G, which can only handle 2 Kbps, to 4G, which supports up to 1Gbps, every new development aims to deliver better speeds. Aside from 5G’s faster speeds, it also allows more users to remain connected, avoiding network congestion during conventions and mass gatherings.
Furthermore, 5G networks diminish latency more than the previous generation. Current 4G connections average from 20 to 40 milliseconds in response time, but 5G could change that by dropping it down to as low as one millisecond.
- Work from anywhere
All these advances in connection speed, reliability and response time mean that users can now reliably work from anywhere. One of the primary constraints of working outside the office is the need for a consistent connection to the corporate network.
Nevertheless, the widespread deployment of 5G technology increases the possibilities for users to work effectively from anywhere. This ensures that users have access to clearer video conferences, near-instantaneous file transfers and even the ability to work with colleagues located in other areas in real time.
- The Internet of Things (IoT) is everywhere
We might not be aware, but the Internet of Things (IoT) is slowly taking over our world. Communication between devices is the main support of this technology, allowing one machine to instruct another for our convenience.
Many homes now have IoT devices because of the availability of a stable Internet connection through Wi-Fi. However, this was not the case until 5G came along. The improved connection reliability of 5G brings IoT to places outside of Wi-Fi coverage.
Besides communication, 5G technology also has the potential to deliver energy to low-power devices, if the IoT device is within the coverage of a 5G network. It can therefore operate without requiring constant recharging.
- Self-driving and other automotive technologies
This industry is one of the biggest beneficiaries of 5G, where almost immediate communication allows vehicles to communicate with other cars and objects. As a result, many manufacturers, including Ford, BMW and Toyota, now integrate 5G antennas in their automobiles.
The combination of roadside IoT and communication devices could eventually lead to true self-driving vehicles. By allowing cars to communicate with each other and with other safety systems, like traffic lights and roadside signs, land transportation can become safer, faster and more efficient.
- Remote Broadcasting
A horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels (4K) of video footage takes up a lot of space and requires massive bandwidth to transmit wirelessly. This is the reason that 5G technology is crucial for entertainment and broadcasting. For instance, 5G drones were used to broadcast the FIFA World Rally Championship.
It can also change the way we see unfolding events. The ability to transmit high-quality footage and the availability of quality cameras on smartphones allows anyone to broadcast live, letting the world know what is happening around them.
More Effective Manufacturing
It is expected that manufacturers will be among the first to deploy 5G technologies because reliable communication is a must for a business to survive these competitive times. Many corporations use systems for data capture and analysis. This can be used to increase efficiency by delivering information where it is needed in real-time.
For example, users can utilise 5G technology in robots, allowing these systems to communicate wirelessly while travelling around the factory floor. With 5G communication, the system can immediately send commands and information to these robots and send them where needed.
Furthermore, advanced technologies like augmented reality and virtual reality can allow engineers to work on systems without requiring them to be on-site.
5G Brings Benefits to Malaysia
5G will change the way people live, work and play. According to Digital National (2023), the technology will bring Malaysia to greater heights through the following benefits:
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband
5G provides the nation with broadband of speeds up to 10 Gbps, making it 100 times faster than 4G.
- Massive Machine Type Communication
The technology enables up to one million connected devices per square kilometre. This allows IoT to be used at a scale never seen before in Malaysia. - Ultra-reliable Low-latency Communication
5G also equips the nation with near-instantaneous reaction times between the push of a button and the required action at the other end. - Network Slicing
By allowing 5G infrastructure development that fits with business purposes, the technology will be able to encourage new revenue creation with better security delivery and improved flexibility. - Fixed Wireless Access
5G also provides broadband connectivity using radio links between two fixed points without needing any wired or physical connections. This allows for high-speed capacity broadband coverage to be supplied to rural areas, which are often left underserved.
Observation
Lightning-fast Internet speeds and seamless connectivity will have the power to uplift businesses and transform our everyday experiences. Now the question is where are we so far?
When the Government first started talking about 5G a few years ago before the COVID-19 pandemic, it was clear that we would not be able to benefit anytime soon. But after the pandemic, industries and Malaysians quickly began using the Internet for video meetings, e-commerce and online events.
This explosive growth meant that there was a real need to expedite the growth of 5G in Malaysia.
The move to start building 5G networks first grew in momentum in 2019. Before the pandemic had even started, the Malaysian Government were already discussing 5G trials to be conducted in Putrajaya and Cyberjaya. In July 2019, the first live field trial by Celcom recorded a maximum Internet speed of 1.256Gbps. Huawei also held a live trial in September 2019 which resulted in a maximum speed of 1.336Gbps, showing the need for improvement.
Digital Nasional Berhad in July 2021 announced a partnership with Ericsson to accelerate the deployment of 5G networks in Malaysia. Ericsson will therefore be the sole partner in the firm, implementing a Single Wholesale Network (SWM) model. The company will build and operate 5G infrastructures in the country and provide access to local telecommunication companies.
Since their announcement in mid-2021, Digital National Berhad has rolled out 5G networks to Cyberjaya, Putrajaya and selected parts of Kuala Lumpur. Further to this, the company also plans to implement 5G networks in major cities within Selangor, Penang, Johor, Sabah and Sarawak covering 37.9 percent of Malaysia’s populated area. It will also expand the rollout plan to Negeri Sembilan, Melaka and Perak. (Yap, 2022)
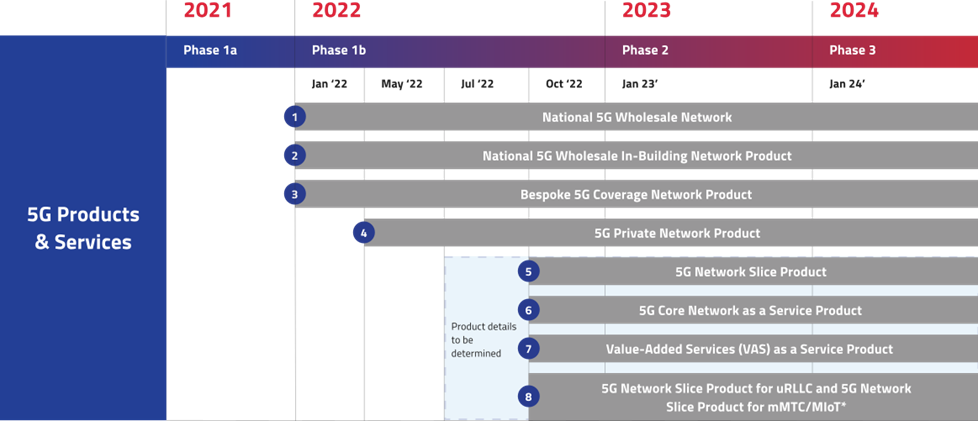
The infographic below illustrates the rollout roadmap providing a view of 5G products and services according to Digital National (2023):
References
Jowi Morales (2022, January 24) 6 Ways 5G is Already Changing the World. https://www.makeuseof.com/ways-5g-changing-the-world/
Gartner Glossary (n.d.) 5G Information Technology https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/5g
Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA, 2022, January 26) 5G Drives Malaysia’s Digitalisation. https://www.mida.gov.my/mida-news/5g-drives-malaysias-digitalisation/
Digital National (2023, May 22) Explore the 5G Rollout https://www.digital-nasional.com.my/interactive-map#map
Matthew Yap (2022, March 15) 5G in Malaysia – Where Are We So Far? https://technave.com/gadget/5G-in-Malaysia-Where-are-we-so-far-29140.html
